Scrawl
Scrawl is a simple command line tool for downloading files referenced on websites using CSS
selectors. This application is not meant to be a replacement for
curl or Wget, but rather a precision tool for grabbing
files when the context in which they are presented is known to. This capability is particularly useful when the path of
the desired file is not known but the URL of the website that links to it is (common for download pages).
Usage
Executing Scrawl with the -help command line argument will trigger online help to be displayed. Below is a more
detailed description of what the parameters do.
attr: The attribute containing the desired download path is specified by this argument.dir: This argument specifies the output directory for downloaded files.vebose: Scrawl will output more details about what it is currently doing when this flag is set.
Example
Let’s say we want to create a script to download the latest Debian package of Anki:
- We load up the homepage and are presented with a big download button as shown in the screenshot below:
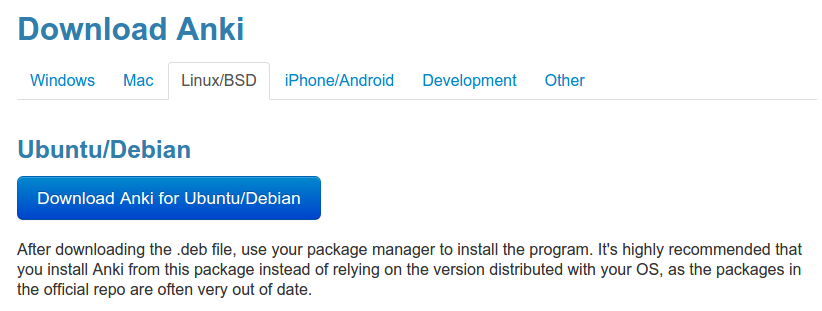
- Let’s copy that link so we can download the latest version with wGet or curl from our script at any time! Hmm, it
looks like the path
http://ankisrs.net/download/mirror/anki-2.0.33.deb has the version number embedded in the
filename. This means that even after a new version of Anki is released, our script will keep getting version
2.0.33 (unless of course it gets deleted). - Let’s inspect the download link in your favorite browser to see what additional information we can get:
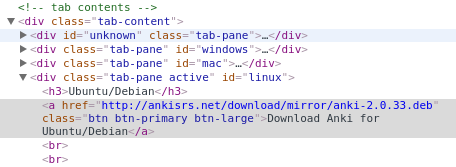
- It appears that we can easily create a selector for this element:
#linux > a:nth-child(2). Note that
Chrome provides the option to copy the CSS selector for any element, making
knowledge of web technology optional for this step. - Now let’s create a simple download and install script:
#!/bin/sh
rm -rf /tmp/anki
mkdir /tmp/anki
scrawl -attr=href -dir=/tmp/anki -verbose http://ankisrs.net/ "#linux > a:nth-child(2)"
sudo dpkg -i /tmp/anki/*.deb
sudo apt-get install -y -f
In this script, we prepare an empty download directory and tell Scrawl to scrape http://ankisrs.net/, extracting
the href property of the download link identified by the CSS selector #linux > a:nth-child(2). We then install
the package and bring in any unsatisfied dependencies.